How to Tell Which Membrane Transport Is Used
Will try to drag the membrane potential toward its negative equilibrium potential. Diffusion Passive Transport 2.
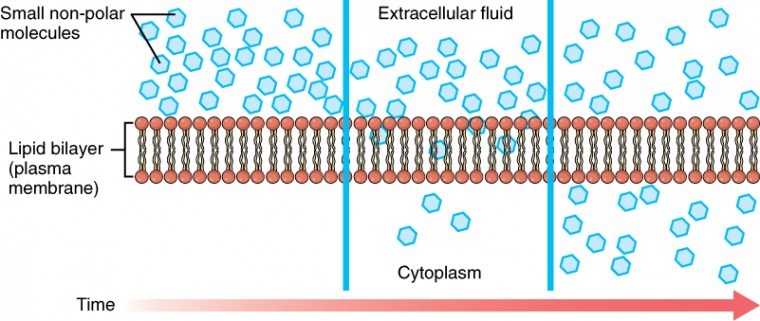
Membrane Transport Anatomy And Physiology
2 Solute particles can traverse the membrane via three mechanisms.

. This movement is used to transport other substances that can attach themselves to the transport protein through the membrane. The regulation of passage through the membrane is due to selective membrane permeability - a characteristic of biological. Membrane transport is dependent upon the permeability of the membrane transmembrane solute concentration and the size and charge of the solute.
As you can see transmembrane channels on either side of the pump allow the ions to flow down their gradient. Passive vs Active Processes. Gerald Litwack PhD in Human Biochemistry 2018.
In cellular biology membrane transport refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such as ions and small molecules through biological membranes which are lipid bilayers that contain proteins embedded in them. Students identify structures within the bilayer and use reasoning to determine how molecules are moving across the membrane in response to a hypertonic solution. Why is membrane potential essential to the survival of all living creatures.
The membrane itself contains polar groups and is therefore electrically charged. Remove a section of tubing from the distilled water and separate the sides to form a tube. There must not be an appreciable difference in the level of the baseline before and after a transport event.
Processes that move substances across membranes can be grouped into two general categories based on whether the process requires an input of cellular energy or not. The transport across cell membrane is classified into three types. The lipid bilayer also houses the Na K pump ATPase pump ion transporters and voltage gated channels and it is the site of vesicular transport.
Active transport requires additional energy often in the form of ATP and results in a nonequilibrium net accumulation uptake of the solute on one side of the membrane. If no energy input is required for the transport then we say particles move via a passive transport process. Flagellar membrane transport events are discriminated from nonspecific cell movement by the following selection criteria.
Types of transport across cell membrane are listed below. Cell Membrane and Transport. In a resting neuron both and are permeant or able to cross the membrane.
Passive facilitated and active transport. For all of the transport methods described above the cell expends no energy. Click again to see term.
Since the cell membrane is made up of a lipid. There must not be appreciable movement of either the flagellum or the cell body. Membrane proteins play a crucial role as transporters in expediting the ions and chemical transfers across the cell membranes.
Bulk transport phagocytosis and pinocytosis Cell Membrane Transport. Types of membrane transport exocytosis facilitated diffusion active transport requiring energy simple and coupled transporters ions and gradients entry of magnesium and divalent ions into cells. Active transport requires energy in the form of ATP solute from lower concentration to higher concentration transport through cell membrane.
The transport of most ions occur more slowly than the non- electrolytes. There are two classes of membrane transport proteinscarriers and channels. In contrast active transport is the movement of substances across the membrane using energy from adenosine triphosphate ATP.
Will try to drag the membrane potential toward its positive equilibrium potential. The cell membrane transport occurs in two major ways like. But H OH penetrate all cell membranes easily.
The structure regulates which ions enter and exit to determine the concentration of specific ions inside of the cell. Whereas transport by carriers can be either active or passive solute flow through channel proteins is always passive. During active transport ATP is required to move a substance across a membrane often with the help of protein carriers and usually against its concentration gradient.
No covalent bonds only hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions. Place a plastic clip across the bottom of the tubing. Membrane proteins that aid in the passive transport of substances do so without the use of ATP.
A membrane is fluid structure with a mosaic of proteins embedded in it. The structure of the cell membrane is designed so that it does not allow free movement of substances. Therefore its fluid however flip flops are rare.
Both form continuous protein pathways across the lipid bilayer. All parts can move laterally. Cell membranes are semi-permeable barrier separating the inner cellular environment from the outer cellular environment.
1 Some of these transport mechanisms require the input of energy and use of a transmembrane. Transport across cell membrane is classified into four ways. Passive and Active Passage Through the Cell Membrane.
This secondary process is also used to store high-energy hydrogen ions in the mitochondria of plant and animal cells for the production of ATP. Based on the transport mechanism and permeability solutes can be divided into three main groups as follows 2. CSqueeze the air out of the bag and place a.
The basic types of membrane transport simple passive diffusion facilitated diffusion by channels and carriers and active transport are summarized in Fig. Cell membrane acts as a barrier to most but not all molecules. You can think of this as being like a.
Describe the plasma membrane structure using the fluid mosaic model Recognize the relative permeability of lipid bilayers to different classes of molecules Compare active and passive transport of molecules Identify the 3 modes of active transport and the different classes of ion channel and carrier molecules. Membrane transportCystic fibrosis is the clinical example related to the principles explored in this chapter. Fill each bag with about 10 ml of solution using a 10 ml graduated pipette.
Small lipophilic lipid soluble molecules that transfer through the membrane by the sole diffusion. This reinforcement worksheet displays a graphic of the cell membrane showing the phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins. The red cell is easily penetrated by Cl and HCO 3.
Passive transport is the movement of substances across the membrane without the expenditure of cellular energy. Secondary active transport moves multiple molecules across the membrane powering the uphill movement of one molecule s A with the downhill movement of the other s B. One of the most common types of.
Many amino acids as well as glucose enter a cell this way.
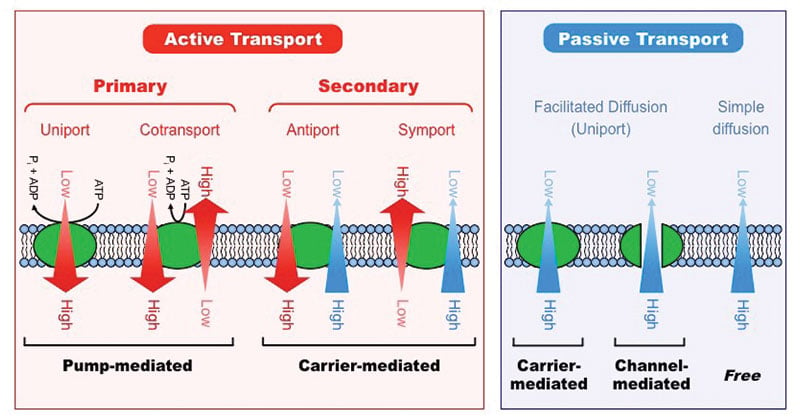
Active Vs Passive Transport Definition 18 Differences Examples

Cell Transport Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
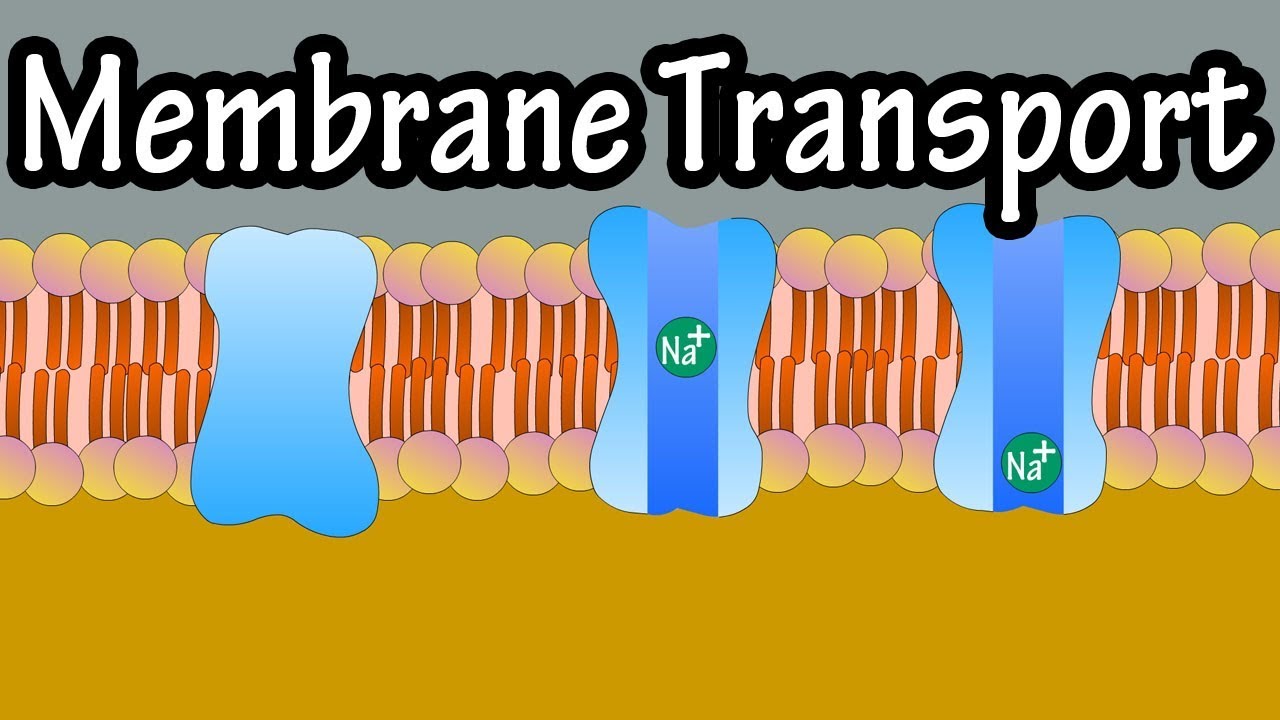
Cell Membrane Transport Transport Across A Membrane How Do Things Move Across A Cell Membrane Youtube
0 Response to "How to Tell Which Membrane Transport Is Used"
Post a Comment